How to Evaluate Hoof Health for Horse Owners
Feb 02, 2015
Published in Saddle Up Magazine February 2015
For many horse owners, evaluating and trimming their horse’s hooves is a task left up to their farrier/trimmer. But how do you know that the person that you have hired is doing a good job? You have to be able to evaluate your horse’s hooves beyond the scope of how sound the horse moves. While soundness in the present is important, the horse’s long term hoof health is also a major factor owners must consider. I see many cases where long term incorrect hoof shape or function has lead to irreversible damage while the horse appeared sound until it was too late to correct. However I also see a lot of horses that I am able to rehabilitate and return to use after a deformed hoof has broken down.
There are 5 key points horse owners can use to evaluate their horses’ hooves:
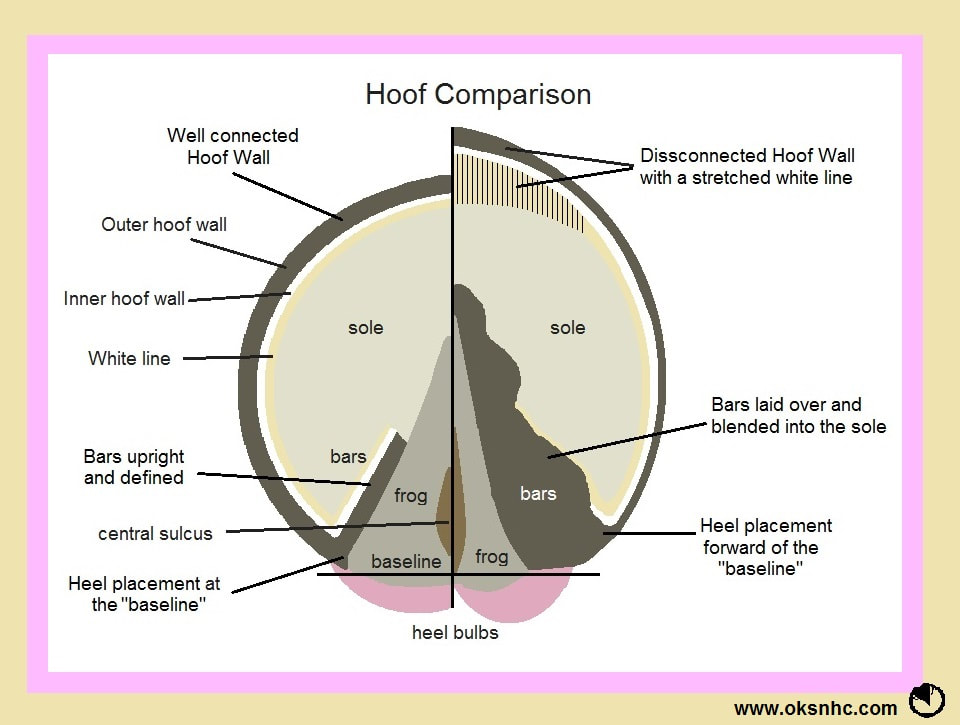
Heel Placement - The heels should be positioned at what we call the baseline. The baseline is an invisible line that runs across the back of the frog and collateral grooves, and in a well-trimmed hoof also aligns with the heels rearmost surface. When heels are allowed to overgrow or migrate forward from this line, the balance of the hoof is distorted and excess stress and tension is placed on the horse’s joints, tendons and ligaments. Long or forward heels can also shorten stride length.
Frog Integrity - When a horse moves forward, their natural stride should allow them to land heel first. If the heels are in the correct position as mentioned above, the heels and frog will contact the ground simultaneously. The frog’s primary function is to protect the digital cushion. The digital cushion lies underneath the hard calloused frog and is a large pad of fatty tissue. The digital cushion absorbs impact and dissipates energy. If the frog is infected with thrush or bacteria, or underdeveloped from long heels keeping it elevated and not touching the ground, this portion of the hoof’s function cannot be performed. Without the energy dissipation of a healthy frog and digital cushion excess stress is placed on the horse’s joints.
Wall Connection - A well connected hoof wall supports the coffin bone and allows the hoof to function as intended. The hoof wall grows downward from the coronet to the ground and should not flare or deviate in angle as it descends. A hoof wall that changes its angle part way down the hoof will have a poor connection and decreased concavity in the sole. A disconnected wall can lead to the coffin bone sinking down into the hoof capsule causing inflammation in the sole resulting in sensitive hooves.
 Sole Thickness - Sole thickness is key to soundness and comfort. A thick sole protects the coffin bone and pads the hoof. The sole should be firm and calloused, you should not be able to flex it when pressing with your fingers. It should have a smooth appearance, and it should have a slight concavity. Concavity varies for each individual horse dependent on their coffin bone shape but the bottom of the hoof should not be flat. A flat hoof signals a balance issue, perhaps in the wall connection or a problem with overgrown bars.
Sole Thickness - Sole thickness is key to soundness and comfort. A thick sole protects the coffin bone and pads the hoof. The sole should be firm and calloused, you should not be able to flex it when pressing with your fingers. It should have a smooth appearance, and it should have a slight concavity. Concavity varies for each individual horse dependent on their coffin bone shape but the bottom of the hoof should not be flat. A flat hoof signals a balance issue, perhaps in the wall connection or a problem with overgrown bars.
Bar Definition - The purpose of the bars are to support the back of the hoof upon impact. The bar is an extension of the hoof wall as it wraps around from the heel surface. The bars should run at a downward slope from the heel to the mid-point of the frog. The bar should also be upright and defined, not laid over or blended into the sole. When bars invade the sole it can cause many different issues, the most common are: sensitivity on hard ground and reoccurring abscessing. In rare cases embedded bar can also cause navicular like symptoms.
Horse owners must learn to recognize what a healthy hoof looks and functions like. Hoof care is a fundamental component of horse ownership and you must know how to recognize a problem before it causes long term damage.